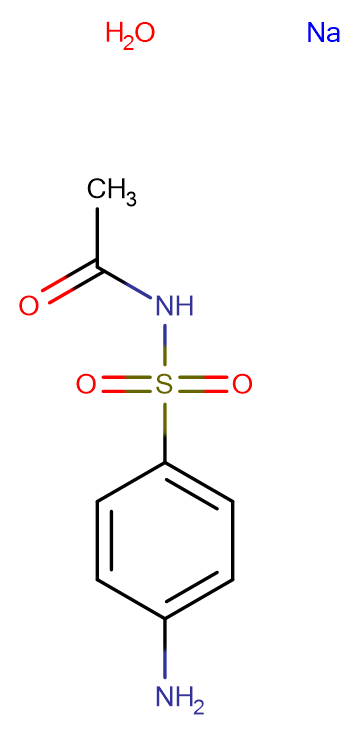
Sulfacetamide sodium salt hydrate
CAS No. 6209-17-2
Sulfacetamide sodium salt hydrate( —— )
Catalog No. M15350 CAS No. 6209-17-2
Sulfacetamide sodium monohydrate is a sulfonamide antibiotic, has been investigated for use in the treatment of pityriasis versicolor and rosacea.
Purity : >98% (HPLC)
 COA
COA
 Datasheet
Datasheet
 HNMR
HNMR
 HPLC
HPLC
 MSDS
MSDS
 Handing Instructions
Handing Instructions
| Size | Price / USD | Stock | Quantity |
| 25MG | 27 | In Stock |


|
| 100MG | 47 | In Stock |


|
| 200MG | 77 | In Stock |


|
| 500MG | 128 | In Stock |


|
| 1G | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
Biological Information
-
Product NameSulfacetamide sodium salt hydrate
-
NoteResearch use only, not for human use.
-
Brief DescriptionSulfacetamide sodium monohydrate is a sulfonamide antibiotic, has been investigated for use in the treatment of pityriasis versicolor and rosacea.
-
DescriptionSulfacetamide sodium monohydrate is a sulfonamide antibiotic, has been investigated for use in the treatment of pityriasis versicolor and rosacea.
-
In Vitro——
-
In Vivo——
-
Synonyms——
-
PathwayAutophagy
-
TargetAutophagy
-
RecptorDHPS
-
Research AreaInfection
-
Indication——
Chemical Information
-
CAS Number6209-17-2
-
Formula Weight254.2
-
Molecular FormulaC8H9N2NaO3S·H2O
-
Purity>98% (HPLC)
-
SolubilitySoluble in Water
-
SMILESO.[Na].CC(=O)NS(=O)(=O)C1=CC=C(N)C=C1
-
Chemical Name——
Shipping & Storage Information
-
Storage(-20℃)
-
ShippingWith Ice Pack
-
Stability≥ 2 years
Reference
1.Hevener KE, et al. J Chem Inf Model. 2009 Jan 27.
molnova catalog



related products
-
Indole-3-Glyoxylyl C...
It is an organic compunds with molecular fomula C10H6ClNO2.
-
DC661
DC661 (DC-661) is a novel dimeric chloroquine (CQ) that is capable of deacidifying the lysosome and inhibiting autophagy significantly better than HCQ, targets palmitoyl-protein thioesterase 1 (PPT1).
-
Ammonium Chloride
Ammonium chloride acts as a small molecule autophagy inhibitor.Ammonium chloride is a pH-regulating, heteropolar compound that can cause intracellular alkalosis and metabolic acidosis, thereby affecting enzyme activity and influencing processes in biological systems.



 Cart
Cart
 sales@molnova.com
sales@molnova.com


